Installation
This section covers the various aspects of installing the Operator.
Important
The Operator is an Enterprise only feature, please contact us for more information.
Prerequisites
Tips
To get the best out of this guide, a basic understanding of Kubernetes concepts is essential.
- A Kubernetes cluster running
v1.23.1or later. - Permission to create resources, deploy the Operator and install CRDs in the target cluster.
- The following CLI tools installed, on your shell’s
$PATH, with$KUBECONFIGpointing to your cluster:- kubectl install guide
- k9s install guide
- Helm 3 CLI install guide
- A valid Operator license. Please contact us for more information.
Configure Helm Repository
Add the Kurrent Helm repository to your local environment:
helm repo add kurrent-latest \
'https://packages.kurrent.io/basic/kurrent-latest/helm/charts/'Install Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs)
The Operator uses Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to extend Kubernetes. You can install them automatically with Helm or manually.
The following resource types are supported:
Since CRDs are managed globally by Kubernetes, special care must be taken to install them.
Automatic Install
It's recommended to install and manage the CRDs using Helm. See Deployment Modes for more information.
Manual Install
If you prefer to install CRDs yourself:
# Download the kurrentdb-operator Helm chart
helm pull kurrent-latest/kurrentdb-operator --version 1.2.0 --untar
# Install the CRDs
helm template -s 'templates/crds/*.yaml' kurrentdb-operator | kubectl apply -f -Expected Output:
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kurrentdbbackups.kubernetes.kurrent.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kurrentdbs.kubernetes.kurrent.io createdAfter installing CRDs manually, you should include the --set crds.enabled=false flag for the helm install command, and include one of --set crds.enabled=false, --reuse-values, or --reset-then-reuse-values for the helm upgrade command.
Caution
If crds.enabled transitions from true to false during an upgrade or rollback, the CRDs will be removed from the cluster, and all KurrentDB and KurrentDBBackup resources will be deleted as well!
Deployment Modes
The Operator can be scoped to track Kurrent resources across all or specific namespaces.
Cluster-wide
In cluster-wide mode, the Operator tracks Kurrent resources across all namespaces and requires ClusterRole. Helm creates the ClusterRole automatically.
To deploy the Operator in this mode, run:
helm install kurrentdb-operator kurrent-latest/kurrentdb-operator \
--version 1.2.0 \
--namespace kurrent \
--create-namespace \
--set crds.enabled=true \
--set-file operator.license.key=/path/to/license.key \
--set-file operator.license.file=/path/to/license.licThis command:
- Deploys the Operator into the
kurrentnamespace (use--create-namespaceto create it). Feel free to modify this namespace. - Creates the namespace (if it already exists, leave out the
--create-namespaceflag) - Deploys CRDs (this can be skipped by changing to
--set crds.enabled=false) - Applies the Operator license
- Deploys a new Helm release called
kurrentdb-operatorin thekurrentnamespace.
Expected Output:
NAME: kurrentdb-operator
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Mar 20 14:51:42 2025
NAMESPACE: kurrent
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: NoneOnce installed, navigate to the deployment validation section.
Specific Namespace(s)
In this mode, the Operator will track Kurrent resources across specific namespaces. This mode reduces the level of permissions required. The Operator will create a Role in each namespace that it is expected to manage.
To deploy the Operator in this mode, the following command can be used:
helm install kurrentdb-operator kurrent-latest/kurrentdb-operator \
--version 1.2.0 \
--namespace kurrent \
--create-namespace \
--set crds.enabled=true \
--set-file operator.license.key=/path/to/license.key \
--set-file operator.license.file=/path/to/license.lic \
--set operator.namespaces='{kurrent, foo}'Here's what the command does:
- Sets the namespace of where the Operator will be deployed i.e.
kurrent(feel free to change this) - Creates the namespace (if it already exists, leave out the
--create-namespaceflag) - Deploys CRDs (this can be skipped by changing to
--set crds.enabled=false) - Configures the Operator license
- Sets the underlying Operator configuration to target the namespaces:
kurrentandfoo - Deploys a new Helm release called
kurrentdb-operatorin thekurrentnamespace
Important
Make sure the namespaces listed as part of the operator.namespaces parameter already exist before running the command (unless you are using the Operator to target the namespace that it will be deployed in to).
Expected Output:
NAME: kurrentdb-operator
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Mar 20 14:51:42 2025
NAMESPACE: kurrent
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: NoneOnce installed, navigate to the deployment validation section.
Augmenting Namespaces
The Operator deployment can be updated to adjust which namespaces are watched. For example, in addition to the kurrent and foo namespaces (from the example above), a new namespace bar may also be watched using the command below:
helm upgrade kurrentdb-operator kurrent-latest/kurrentdb-operator \
--version 1.2.0 \
--namespace kurrent \
--reuse-values \
--set operator.namespaces='{kurrent,foo,bar}'This will trigger:
- a new
Roleto be created in thebarnamespace - a rolling restart of the Operator to pick up the new configuration changes
Deployment Validation
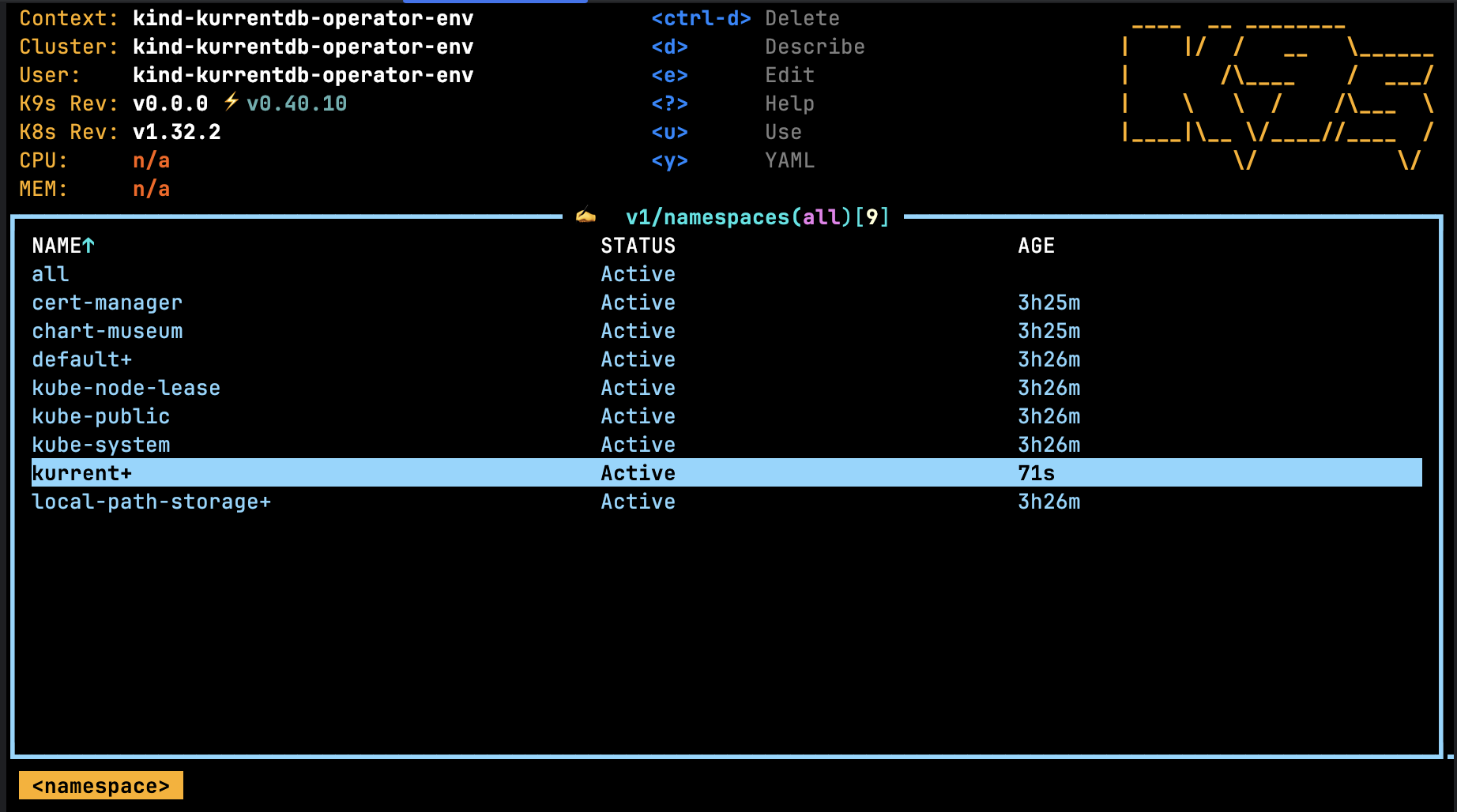
Using the k9s tool, navigate to the namespace listing using the command :namespaces. It should show the namespace where the Operator was deployed:
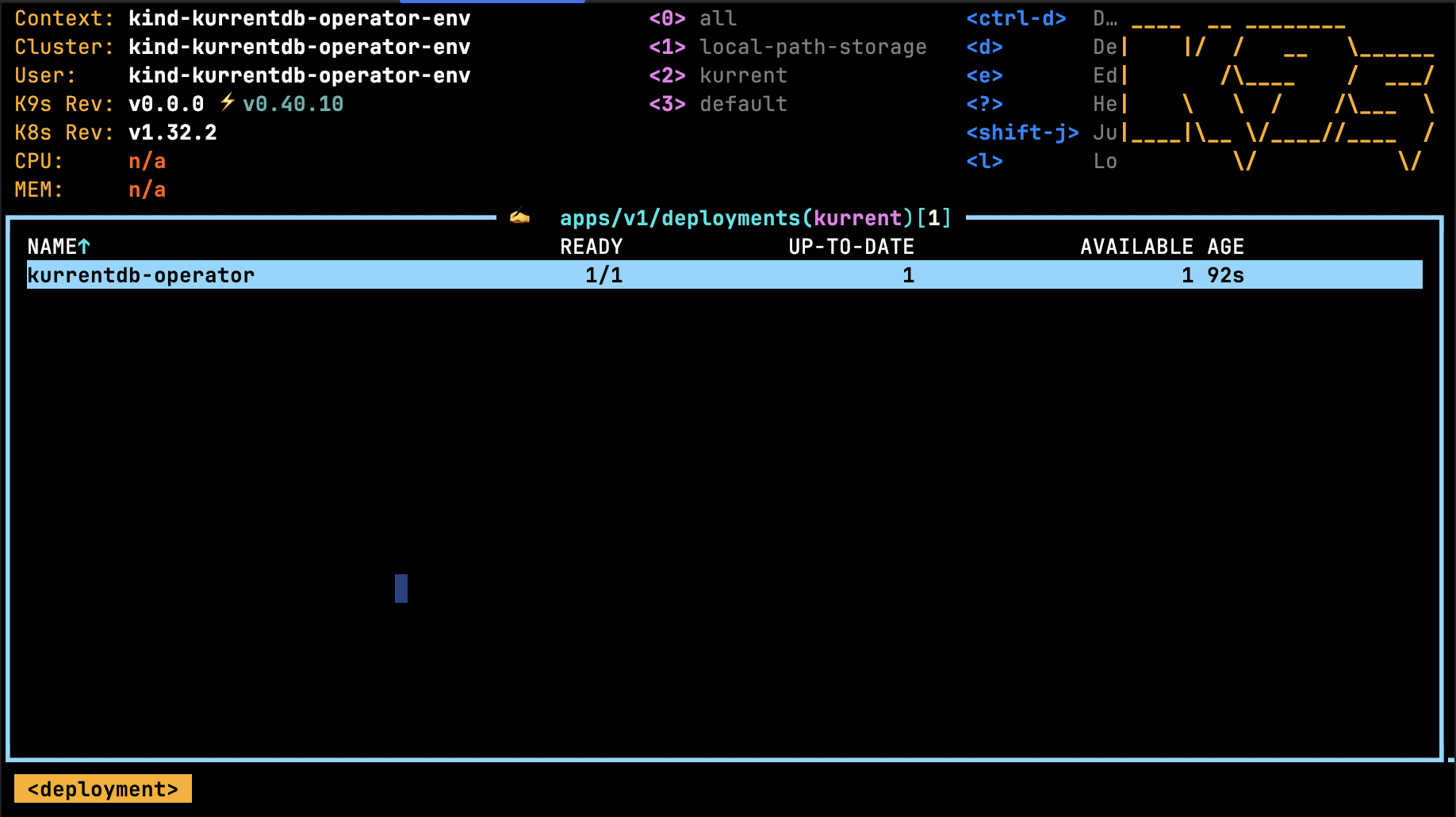
After stepping in to the kurrent namespace, type :deployments in the k9s console. It should show the following:
Pods may also be viewed using the :pods command, for example:
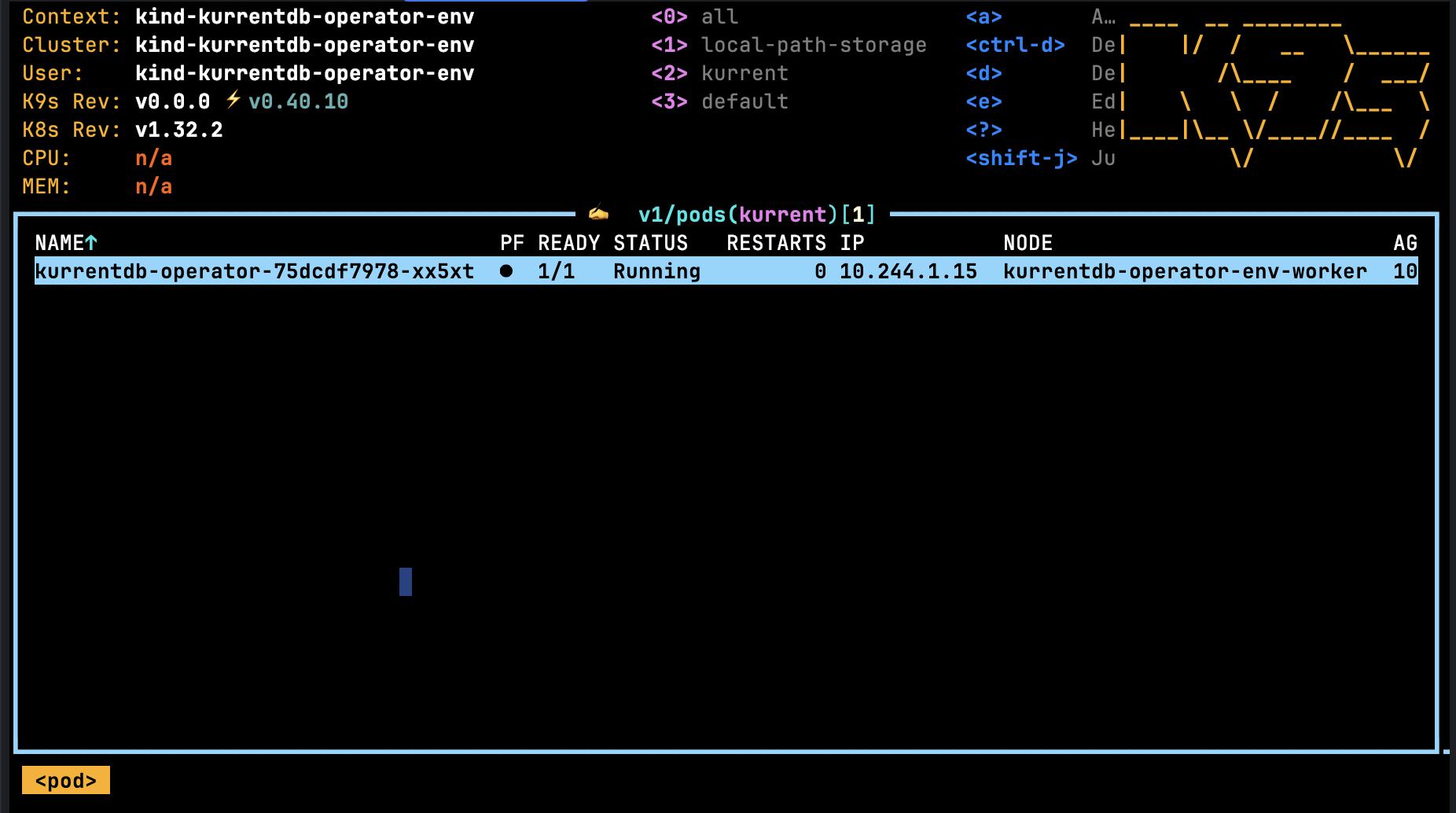
Pressing the Return key on the selected Operator pod will allow you to drill through the container hosted in the pod, and then finally to the logs: