Database Backup
The sections below details how database backups can be performed. Refer to the KurrentDBBackup API for detailed information.
Prerequisites
Tips
To get the best out of this guide, a basic understanding of Kubernetes concepts is essential.
Before installing and executing the Operator, the following requirements should be met:
- The Kubernetes cluster already has a volume snapshot class configured.
- The Operator has been installed as per the Installation section.
- A
KurrentDBhas already been deployed that requires backing up. - The following CLI tools are installed and configured to interact with your Kubernetes cluster. This means the tool must be accessible from your shell's
$PATH, and your$KUBECONFIGenvironment variable must point to the correct Kubernetes configuration file:
Important
With the examples listed in this guide, the Operator is assumed to have been deployed such that it can track the kurrent namespace for deployments.
Backing up the leader
Assuming there is a cluster called kurrentdb-cluster that resides in the kurrent namespace, the following KurrentDBBackup resource can be defined:
apiVersion: kubernetes.kurrent.io/v1
kind: KurrentDBBackup
metadata:
name: kurrentdb-cluster
spec:
volumeSnapshotClassName: ebs-vs
clusterName: kurrentdb-clusterIn the example above, the backup definition leverages the ebs-vs volume snapshot class to perform the underlying volume snapshot. This class name will vary per Kubernetes cluster/Cloud provider, please consult with your Kubernetes administrator to determine this value.
The KurrentDBBackup type takes an optional nodeName. If left blank, the leader will be derived based on the gossip state of the database cluster.
The example above can be deployed using the following steps:
- Copy the YAML snippet above to a file called
backup.yaml - Run the following command:
kubectl -n kurrent apply -f backup.yamlOnce deployed, navigate to the Viewing Backups section.
Backing up a specific node
Assuming there is a cluster called kurrentdb-cluster that resides in the kurrent namespace, the following KurrentDBBackup resource can be defined:
apiVersion: kubernetes.kurrent.io/v1
kind: KurrentDBBackup
metadata:
name: kurrentdb-cluster
spec:
volumeSnapshotClassName: ebs-vs
clusterName: kurrentdb-cluster
nodeName: kurrentdb-1In the example above, the backup definition leverages the ebs-vs volume snapshot class to perform the underlying volume snapshot. This class name will vary per Kubernetes cluster, please consult with your Kubernetes administrator to determine this value.
The example above can be deployed using the following steps:
- Copy the YAML snippet above to a file called
backup.yaml - Run the following command:
kubectl -n kurrent apply -f backup.yamlOnce deployed, navigate to the Viewing Backups section.
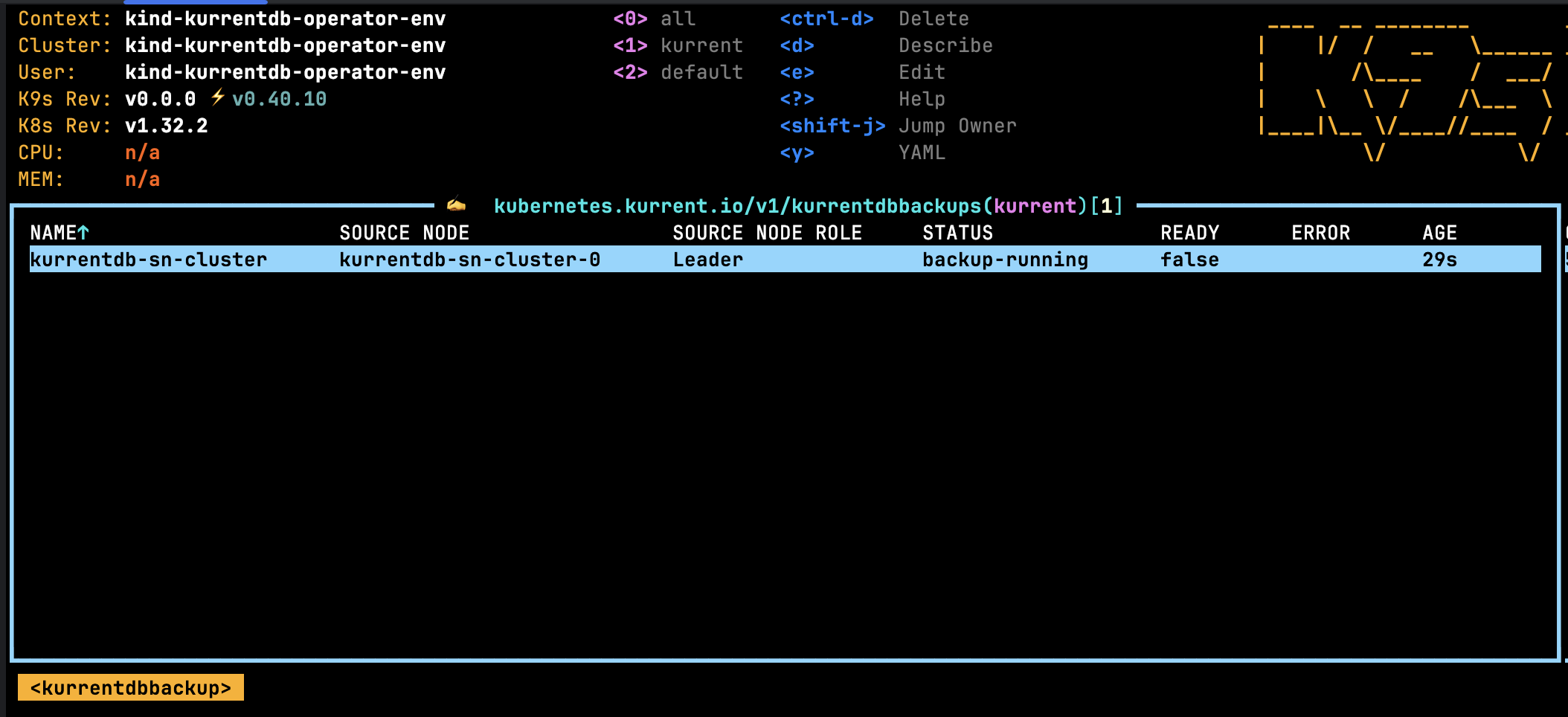
Viewing Backups
Using the k9s tool, navigate to the namespaces list using the command :namespaces, it should show a screen similar to:
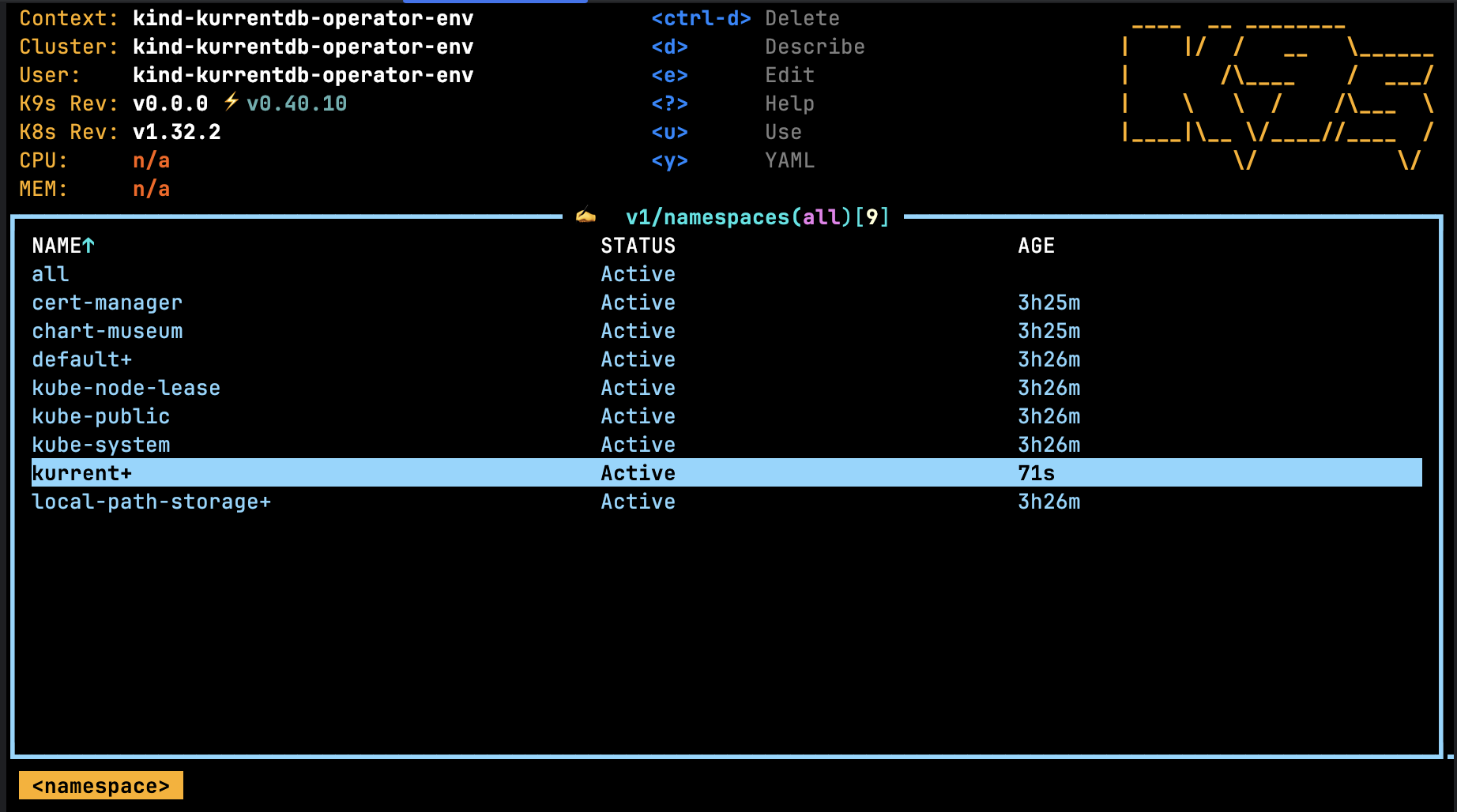
From here, press the Return key on the namespace where the KurrentDBBackup was created, in the screen above the namespace is kurrent. Now enter the k9s command :kurrentdbbackups and press the Return key. The following screen will show a list of database backups for the selected namespace.